Call Us: +91 7217211004 | +91 9175456781
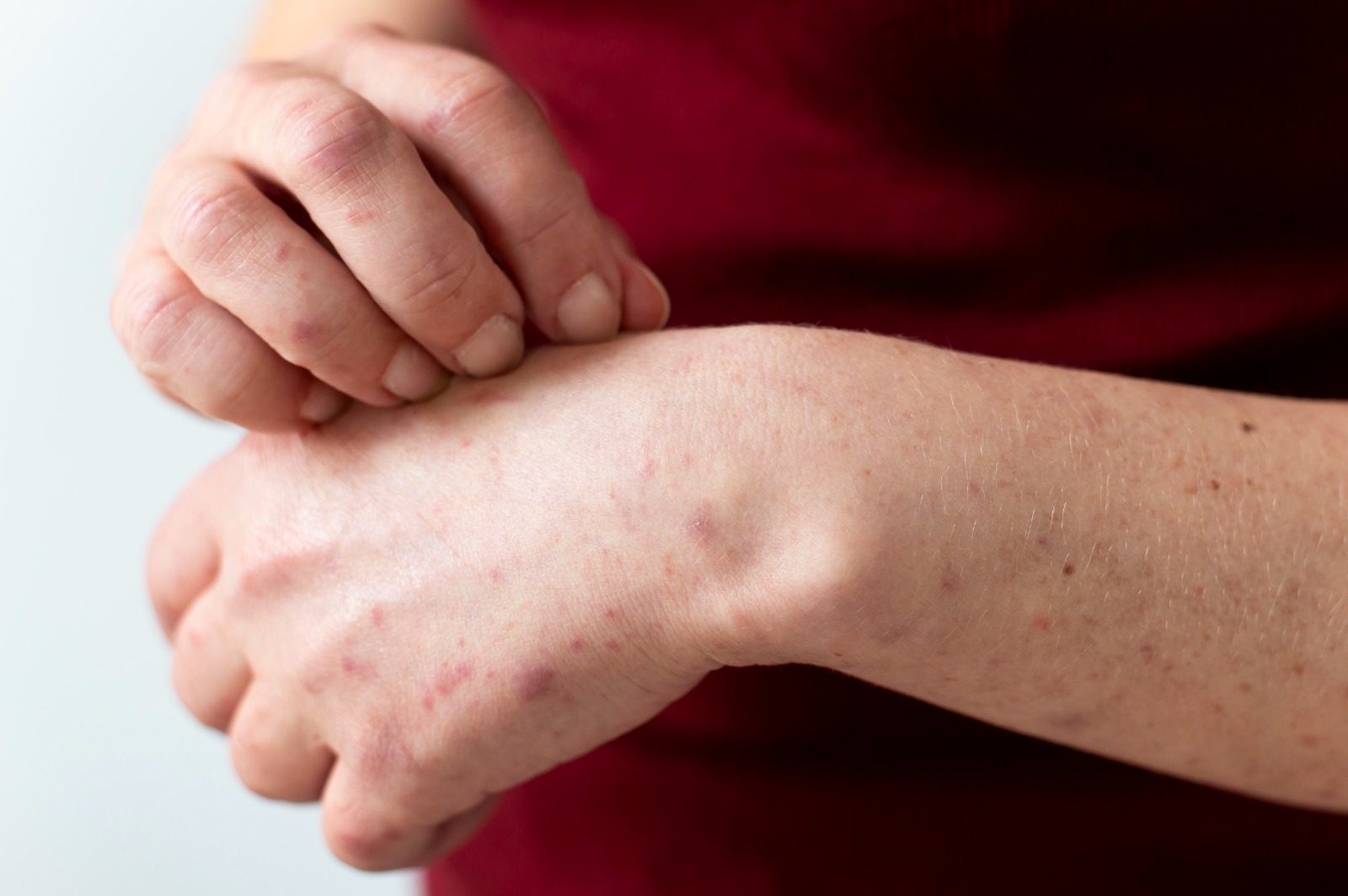
Folliculitis is a skin condition caused by an inflammation of one or more hair follicles in a limited area. It typically occurs in areas of irritation, such as sites of shaving, skin friction, as well as rubbing from clothes. In most cases of folliculitis, the inflamed follicles are infected with bacteria, especially with Staphylococcus organisms, that normally live on the skin.
The most common factors that contribute to the development of folliculitis include:
- Irritation from shaving
- Friction from tight clothing
- A pre-existing skin condition, such as eczema, acne, or another dermatitis (inflammation of the skin)
- Injuries to the skin, such as abrasions
- Extended contact from plastic bandages or adhesive tape
at Skin and Scalps Clinic the treatment for folliculitis depending on the type and severity of the condition, what self-care measures have already been tried and your preferences.
- Creams or pills to control infection. For mild infections, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic cream, lotion or gel. Oral antibiotics aren’t routinely used for folliculitis. But for a severe or recurrent infection, your doctor may prescribe them.
- Creams, shampoos or pills to fight fungal infections. Antifungals are for infections caused by yeast rather than bacteria. Antibiotics aren’t helpful in treating this type.
- Creams or pills to reduce inflammation. If you have mild eosinophilic folliculitis, your doctor may suggest you try a steroid cream to ease the itching. If you have HIV/AIDS, you may see improvement in your eosinophilic folliculitis symptoms after antiretroviral therapy.
